What is the Salesforce API Access Control feature and why is it very good for security?
- Doug Merrett
- Jul 23, 2025
- 4 min read
Updated: Jul 24, 2025
TL;DR; Get the API Access Control feature enabled in your org, Install all your Connected apps, change their app policies to Admin approved users are pre-authorized and add an “allow access” permission set to all users who need access and then turn on API Access Control. This will prevent rogue apps connecting to your org.
How do you stop employees from connecting unknown OAuth apps or even SOAP/REST apps to your Salesforce org? A little known Salesforce capability called API Access Control.
With Salesforce’s API Access Control, you are able to stop unapproved OAuth connected apps from connecting and unapproved users from using approved connected apps.

The highlighted options, when enabled, will block access to internal and external users accessing unapproved apps.
You have probably now gone to see what your current settings are for API Access Control, however it is most likely not activated in your org. My guess why Salesforce has not activated it by default is because just turning API Access Control on without configuring other parts of Salesforce will stop most, and maybe all of your API integrations from working.
You need to raise a case with Salesforce Technical Support to get the feature activated in your org. When it has been activated in your production org, you are able to get it into your Sandbox orgs, without refreshing them, by using the Matching Licences facility in the Company Information section of Setup in the sandbox.
Do not rush in and click the two highlighted checkboxes as this could cause all your currently connected apps to fail — you need to do some other work first — and preferably in a sandbox to make sure it works as you expect.
Either Install or Block all current Connected Apps.
The first step is to go to Connected Apps OAuth Usage in Setup and click either Install (for apps you approve) or Block (for apps you do not approve). Install is a bit of a misnomer as the apps are already connected to your org — installing them just gives you the ability to manage policies on who can use them. Here is a picture of my org with Dataloader.io highlighted as it is the only app that is not installed or blocked. I will install it as I want to allow some users in my org permission to run it.

Edit the App Policies to limit access to just the users you want
For each application that is now installed, click the Manage App Policies link. This will take you to this page:
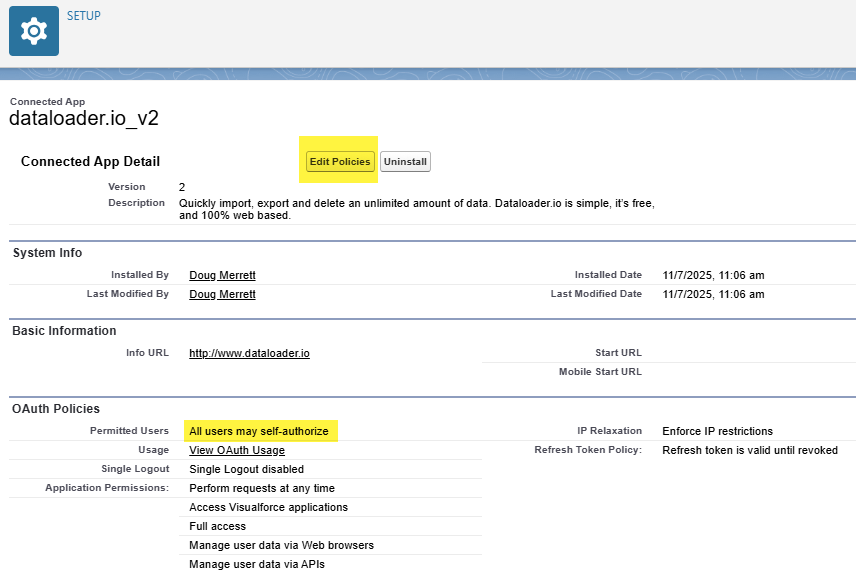
The Permitted Users will be set to All users may self-authorize. This is not what we want — we want to limit access to the app to only a few users in this case. If you want to allow all users access, then you can leave it as it is. You may want to do this for Salesforce for Android for example.
When you click on Edit Policies, you can change the Permitted Users to Admin approved users are pre-authorized. You may also want to change the Refresh Token Policy to Expire refresh token after 7 Days to force users to re-authenticate every 7 days (or whatever timeframe you prefer).
Now that you have limited access to approved users only, you need to configure which users these are. There are two ways to do this — either by profile or by permission set (or both). In this case, I want all System Administrators to be able to access Dataloader.io as well as one super user. To do this I will create a permission set called Allow Dataloader.io and add it to our super user. The permission set does not need to have any permissions, it just needs to exist. I use the naming convention of Allow followed by the Connected App’s name. Add the Profile and/or Permission Set to the related lists that have now appeared lower down the page.
The ability to grant a Permission Set for a limited timeframe is very handy in this use case — you could give our super user access to Dataloader.io for a week and then automatically remove that access by having the Permission Set time out.

Now you have Installed or Blocked every connected app and configured the allowed users for each Installed app, you are ready to enable the API Access Control checkbox(es).

And that is it. Now any time someone tries to connect an unapproved connected app, it will fail. And if someone who is not authorised to use an approved app tries to connect, it will also fail.
As mentioned, this will also block users from using standard SOAP API Access using username and password. For example, developers using SoapUI to assist in developing integrations. In this case, you can add the Use Any API Client permission to their user via a Permission Set. Be very careful with this though, as it bypasses the API Access Control setting as well… Another excellent use of a time-limited Permission Set.





Comments